Taxonomy: Fungi, division of oomycetes.
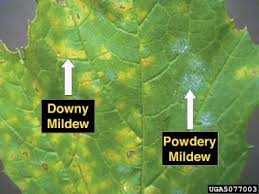
Description: A common disease in Zimbabwe. Downy mildew refers to any of many types of oomycete microbes that are obligate parasites (require a living host) of plants. Initial symptoms include large blocky, yellow areas visible on the upper surface. As lesions develope, they expand rapidly and go brown. The under surface of infected leaves appear water soaked. If you look closely purple-brown mold becomes apparent. Small spores shaped like footballs can be observed among the mold with a magnifine glass.
Distribution on the plant: In disease-favorable conditions, downy mildew will spread rapidly, destroying leaf tissue without affecting the stem of the plant.
Lifecycle: Obligate parasite - requires a living host plant to reproduce.
Determent to crops: Injury to the leaf tissues.
Monitoring remarks: Check for early signs on the low leaves of the crop. Monitor more frequently once the crop canopy has closed, and during periods of persistent rainfall.
Action threshold: Preventative fungicides recommended. Take curative action at early signs of the disease.
Control general remarks: Spray broad spectrum fungicides. Alternate fungicides from different chemical groups to avoid chemical resistance.
Contact a Cropserve agronomist for further information.