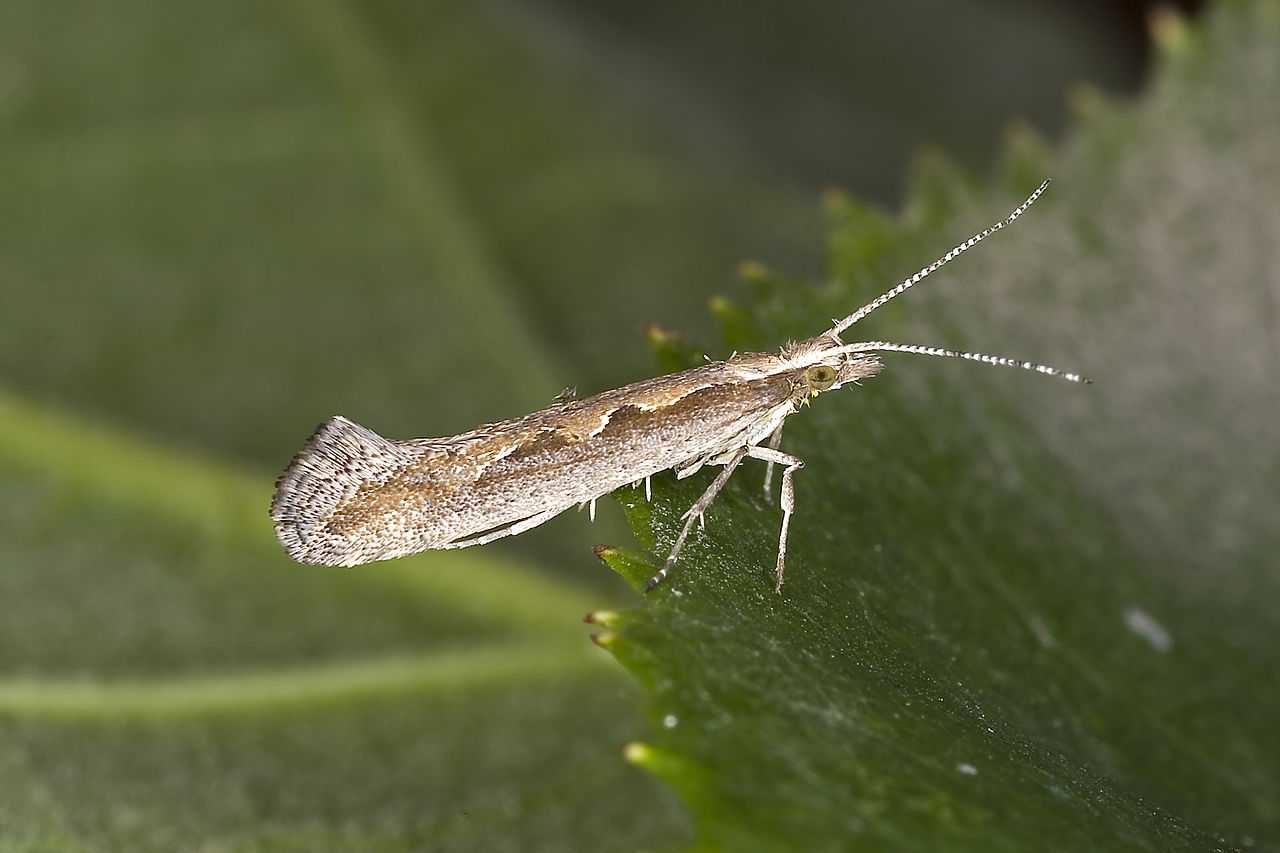
TAXONOMY: Lepidoptera (Order). also internationally commonly called the "Cabbage Moth".
DESCRIPTION: Problematic in cabbages and other brassicas in Zimbabwe. The females lay eggs only on the leaves of the cabbage and do not discriminate between young and more developed leaves. Females are more likely to deposit their eggs on a host with a larval infestation. Larvae damage leaves, buds, flowers, and seed buds of cultivated cruciferous plants. Although the larvae are small, they can occur in great numbers and cause complete removal of foliar tissue except for the leaf veins. This is damaging to small seedlings and may interfere with head formation in cabbage, broccoli, and cauliflower.
PEST IDENTIFICATION (Adult): This small moth is grey and brown coloured. It can potentially be identified by a cream-coloured band that may be present in the shape of a diamond on its back. The diamondback moth has a wingspan of about 15mm and a body length of 6mm. The forewings are narrow, brownish grey and lighter along the anterior margin, with fine, dark speckles. A creamy-coloured stripe with a wavy edge on the posterior margin is sometimes constricted to form one or more light-coloured diamond shapes, which is the basis for the common name of this moth. The hindwings are narrow, pointed toward the apex, and light grey with a wide fringe. The ends of the wings can be seen to turn upward slightly when viewed from the side. The antennae are easily visible. Diamondback moths overwinter as adults among crop residues of cruciferous crops, and active adults may be seen during warm periods at any time during the winter in temperate areas.
PEST IDENTIFICATION (Pupa): The yellowish pupae are about 8 mm long and are wrapped in a loose silk cocoon. They are usually found on the lower or outer leaves of the food plant, but on cauliflower and broccoli, pupation may occur in the florets.
PEST IDENTIFICATION (Larvae): The larvae have four instars, each with an average development time of about four days. The larval body form tapers at both ends. The larvae have a few short black hairs and are colourless in the first instar, but pale or emerald green with black heads in later instars.
PEST IDENTIFICATION (Egg): The eggs are oval and flattened, measuring 0.44 mm long & 0.26 mm wide. They are yellow or pale green at first but darken later. They are laid singly or in groups of two to eight eggs in depressions on the surface of leaves. Females may deposit up to 300 eggs in total, but average production is probably half that amount. The larvae emerge from the eggs in about six to seven days.
DISTRIBUTION ON PLANT: Well distributed on the plant.
LIFECYCLE: The moth has a short life cycle (14 days at 25 °C). Moth - Egg - Larvae - Pupa.
DETRIMENT TO CROPS: Chewing pest at larval growth stages.
MONITORING REMARKS: Use DBM pherolure with delta trap to monitor this pest.
ACTION THRESHOLD: Spray 1 week after identifying an influx of moths.
CONTROL REMARKS: In areas that have bad infestations of DBM, use Last Call DBM or Trap-All DBM to break the life cycle of the pest. Scout regularly and use selective sprays to kill the pest at Larval growth stages (>4th instar).
Contact a Cropserve agronomist for further information.