TAXONOMY: Lepidoptera (order). Common names African Bollworm / Budworm / Heliothis. Scientific name: Helicoverpa armigera.
DESCRIPTION: The bollworm is very variable in both size and colour.
PEST IDENTIFICATION (Moth): The body length varies between 12-20mm with a wingspan of 30–40mm. The fore wings are yellow/orange in females and greenish/grey in males, with a slightly darker transversal band in the distal third. The hind wings are a pale yellow with a narrow brown band at the outer edge and a dark round spot in the middle.
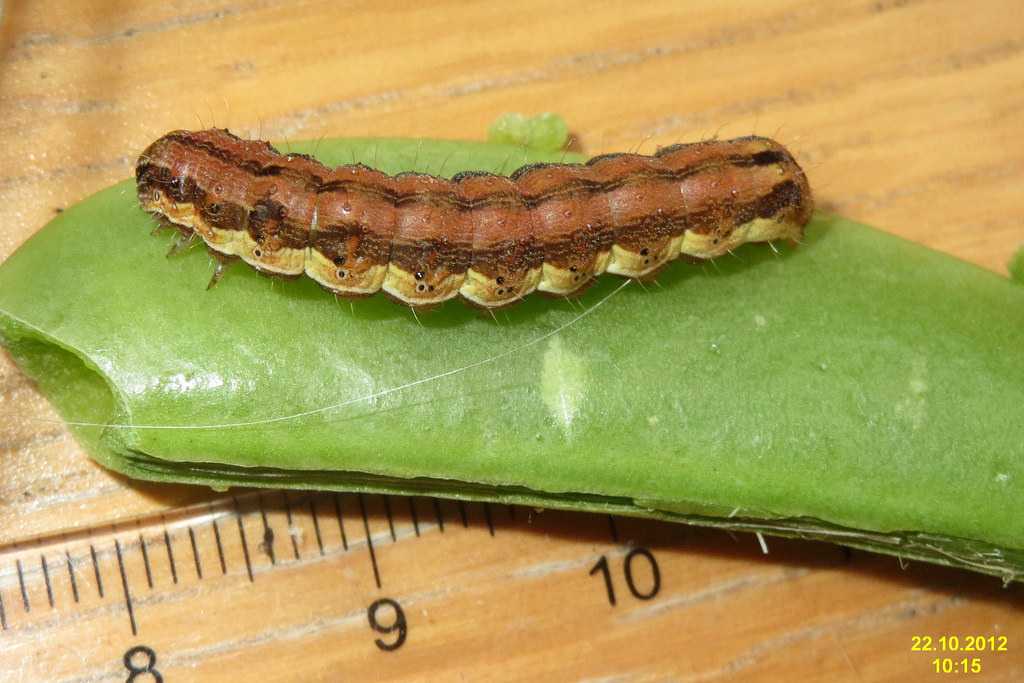
PEST IDENTIFICATION (Larvae / Caterpiller): The caterpillars colouring is variable but mostly greenish and yellow to red-brown. The head is yellow with several spots. Three dark stripes extend along the dorsal side & one yellow light stripe is situated under the spiracles on the outer side.
PEST IDENTIFICATION (Egg): no remark.
DISTRIBUTION ON PLANT: Leaf and pods.
LIFECYCLE: The female bollworm can lay several hundred eggs, distributed on various parts of the plant. Under favourable conditions, the eggs can hatch into larvae within 3 days and the whole lifecycle can be completed in just over a month. The eggs are spherical and 0.4-0.6mm in diameter, and have a ribbed surface. They are white, later becoming greenish. The larvae take 13-22 days to develop, reaching up to 40mm long in the sixth instar.
DETRIMENT TO CROPS: Chewing pest, can cause foliar damage and get into vegetable fruit.
MONITORING REMARKS: Use pheromone lures and traps to monitor this pest.
ACTION THRESHOLD: Take action within a week after identifying a rapid influx of moths in the traps.
CONTROL REMARKS: Highly problematic during warm conditions.